Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland is situated at the front of the neck, below the voice box or larynx (Adam's apple).
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones that are important for:
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones that are important for:
- Development and growth
- Regulation of body temperature
- Energy expenditure & metabolism
- Heart rhythm and regulation of breathing
- Ovulation & normal pregnancy
Pregnancy
Thyroid dysfunction can affect a person at any age. Women are more susceptible than men.
During pregnancy, imbalances in thyroid hormones can cause:
During pregnancy, imbalances in thyroid hormones can cause:
- Miscarriages
- Foetal growth restriction and cognitive impairment
- Maternal high blood pressure
- Premature delivery
- Placental abruption
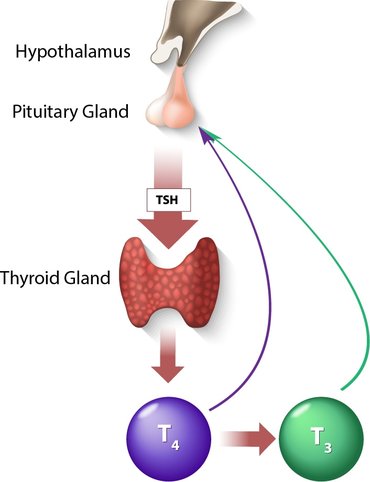
How are thyroid hormones made and regulated?Thyroid hormones (T4 and T3) are made by the thyroid gland from iodine rich food.
The amount of thyroid hormones secreted by the thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland, via a hormone called thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Feedback loop Although the pituitary gland is the control centre, circulating thyroid hormones are fed back to the pituitary gland to modulate the amount of TSH released, thus keeping the thyroid hormones in the normal range.
|
|
|
Too much or too little is not good for youTransient and subtle changes in your thyroid gland may go unnoticed. Overt changes rarely does as thyroid hormones control many aspects of your body.
Investigations and DiagnosesThyroid disease can be diagnosed from history, physical examination and careful interpretation of blood tests and thyroid imaging.
TreatmentTreatment advice depends on the underlying cause, severity of presentation and whether you’re pregnant or planning to fall pregnant. |